SEO for Photographers
Updated October 20th, 2023.
Introduction to SEO
If you’ve followed me on Twitter or Facebook for a while, you might know that I’m a major proponent of Search Engine Optimization being a major portion of the typical marketing strategy for photographers. It’s also grown into a consulting business where I help photographers and companies improve their visibility in search engines.
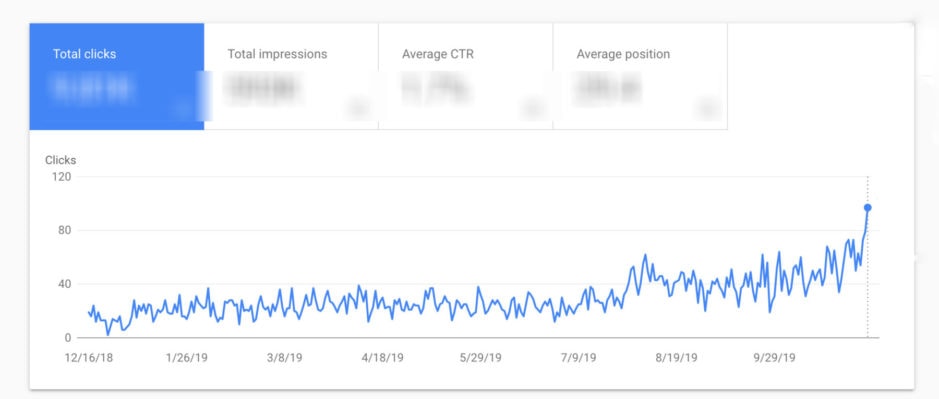
Organic traffic from Google is how I book well over half of my weddings at home in Portland and in places like Big Sur and Yosemite. While SEO can get extremely technical, it doesn’t have to be. Over the past 7 years of teaching these strategies, I’ve found ways to simplify the most important aspects into digestible and actionable techniques. If you’re new to SEO, or don’t even have a clue what that is.. let’s get you started on your journey.
To join the discussion, check out my Facebook Group. If you’d like to master SEO, take a look at the SEO for Photographers Course that I created with Corey Potter from Fuel Your Photos.
How to improve the SEO of your photography website in 6 Steps:
- Image size and Compression. You need to make sure that users aren’t downloading larger images than are being displayed for their device. You also need to compress these files more aggressively than most photographers are used to for print or display.
We recommend Short Pixel for compression. It has a Wordpress plugin that can automatically compress new uploaded images and go back through your media library and fix all of your older images. - Stop Competing with Yourself. Make sure that you only have one page on your site that is optimized for each topic that you’re targeting.
Also, check to make sure that your SEO plugin or website platform settings aren’t appending the main target keyword to every page’s title tag. - Mobile First. Design your site from a mobile perspective first. Not only are the majority of users now accessing photography sites from their phone, but Google crawls using a mobile user agent.
Mobile devices also have a harder time loading complex websites or large pages. Slow mobile sites can be penalized.
If you hide content on your mobile version, Google will think it is unimportant. Don’t forget to check Mobile Friendliness and Pagespeed Insights. - Clean up your Indexation. You want to minimize how many low quality pages you have indexed by Google.
These are often tag archives, category archives, image attachments, theme example pages, client only pages, hidden pages, pricing guides, etc. - Pagespeed. Make sure you have proper caching (we like WP Rocket). We also recommend a modern lazy loading solution (wp rocket handles this well) and fast hosting.
We write more about our favorite hosting options here. - Broken Links. It’s never great to link out to broken pages. Over time, it is inevitable that vendors you worked with in the past, or people who commented on your site, will let their domain expire.
It’s a good idea to scan for broken links at least every 6-12 months. You can use a tool like Screaming Frog or a website like Broken Link Check.
Free 7 Day SEO Challenge
Corey and I recently created a 7 day SEO challenge. Each day, you get a simple and actionable lesson in your inbox. The lessons include a 3-5 minute Youtube video and one task for you to take.
If you complete all 7 days, you get a free copy of our e-book ($99 value).
Google Search Console
Before we start, I need to to go to Google Search Console and verify your website. This verification has to happen before you can start collecting search data straight from google. It will tell you if you have errors or issues with your site, what your organic traffic is, what pages searchers are visiting, what queries they’re using to find those pages, and more. It’s one of the most important tools in your SEO toolbox.
Here is a guide: https://www.fuelyourphotos.com/guide-to-search-console/
SEO Quick tips on Youtube
What is SEO?
Simple answer: The art and science of optimizing websites for organic traffic from search engines.
A bit more nuance: SEOs must now have to optimize for users AND search engines. Covering a broad spectrum of disciplines, from technical optimization to content, content marketing, conversion optimization, user experience, and taxonomy. On top of that, Organic Traffic isn’t (and shouldn’t be) exclusive to get from Google, but also Youtube, Bing, and other platforms.
History of SEO
This story probably isn’t starting off quite how you expected, but the band in the photograph below is Jefferson Starship. In 1995, the built a fancy new website. Their manager was excited to show it off to a venue promoter.. but when they searched for it on a search engine.. they didn’t appear until page 4 or 5. The manager furiously called the website builder and asked them what was going on!
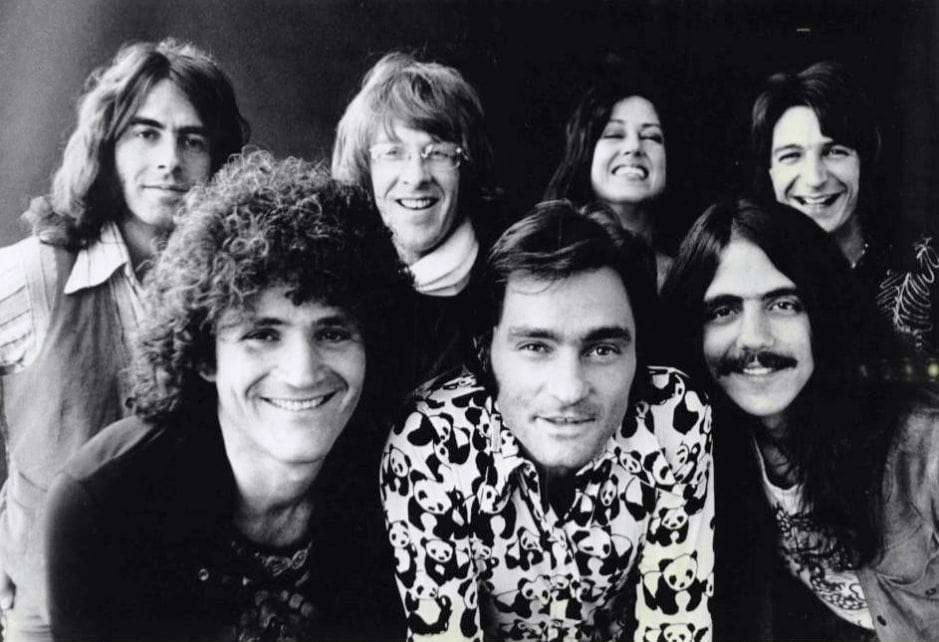

The web guy was quickly able to figure out that how many times a keyword appeared on a page greatly influenced the rankings of the search engine. His strategy to improve rankings was quite simple, tiny black text on a black background that repeated the bands name. The band’s rankings skyrocketed and SEO was born.
Search engines have grown much more complex and this type of tactic wouldn’t work in 2020, but it’s interesting to see it’s early start.
Basic Information Retrieval
The hardest challenge for the early search engines was simply crawling the internets’ pages, indexing them, and giving users somewhat accurate results to queries.
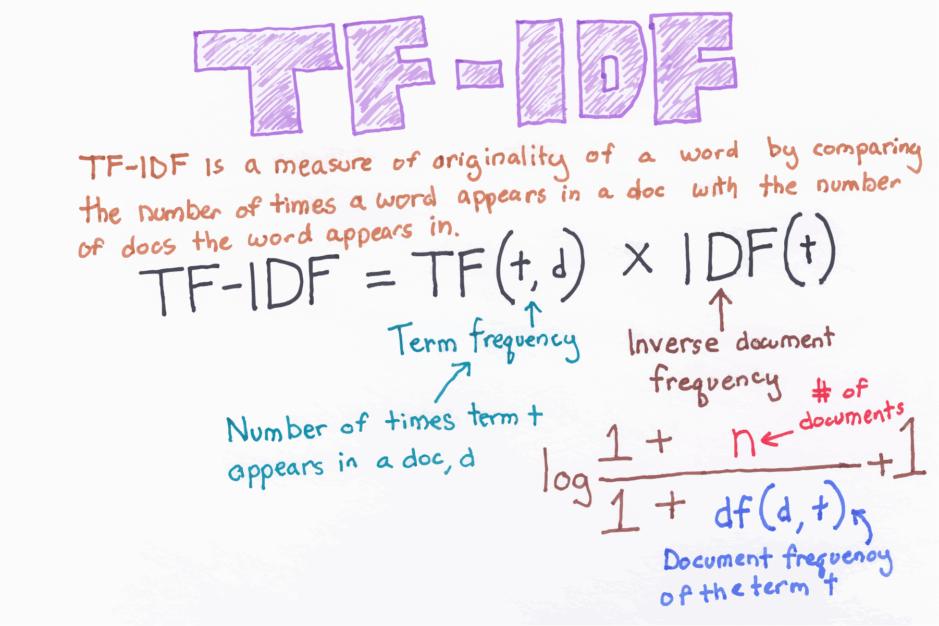
There are a few concepts and equations that laid the groundwork for modern search. TF-IDF is one of them. The concept figuring out how relevant a term is to a page and then comparing that to how many times that term shows up across the entirety of pages was incredibly powerful.
The groundbreaking TF-IDF equation was first created by Karen Spärck Jones in 1972.
Where Search is Now
Now, you can make a query using your Google smart speaker, it will decipher what task you want to accomplish, and in some cases will try to accomplish it for you. One real world example is making a dinner reservation. It will see if the restaurant is open, what the restaurant’s contact info is, make a call using an AI voice, talk to the person on the other end of the phone, create a reservation for your time and number of guests, and let you know it’s booked.
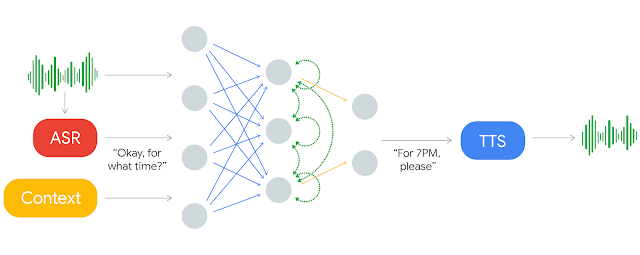
More about Google Duplex here.
What SEO isn’t

The example before of Jefferson Starship jamming keywords into their page and hiding them with a font the same color as their background wouldn’t work these days.
Search engine algorithms and manual testers are great at spotting this type of abuse and penalizing those sites.
Now, you must create actual valuable content for your users. The whole “write for users, not algorithms” mantra is more true than ever.
Google’s Ranking Process
Here is an example from new hires training at google. It explains that each page has a “bid” calculated. This bid is calculated by multiplying hundreds of factors together. Each factor can have multiple signals. (The below example is just a guess at what that could look like)
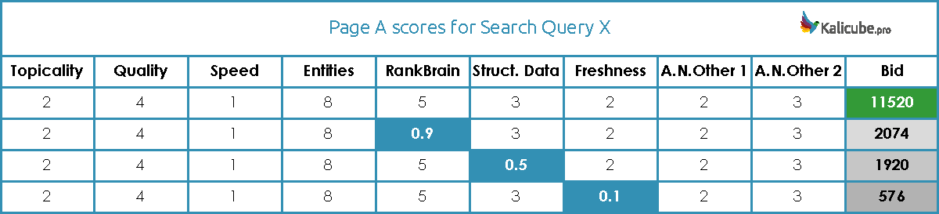
- Factor scores are multiplied across with a max bid score of 2^64.
- There are hundreds of factors and can be multiple signals per factor.
- A low or zero score on one factor will be crippling.
- There is a second wave of scoring to remove spam.
- There is a third wave of scoring to decide search results features (featured snippets, etc)
You can read more here: https://www.searchenginejournal.com/how-google-search-ranking-works/307591/
SEO Hierarchy of Needs
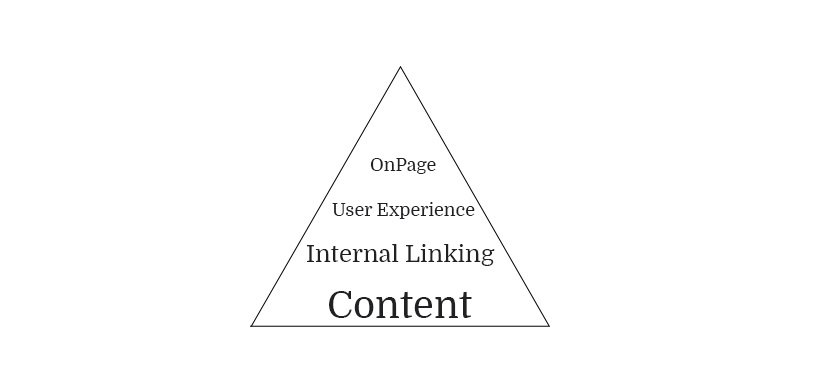
Most SEO guides concentrate almost completely on OnPage factors that you can optimize. We’ll dive into those in a moment, but first we must talk about the foundation of our rankings.
Without quality content, you are unlikely to have long-term rankings and traffic. We go into great detail on how to create this type of content in our SEO Course.
The basics are that you want to have well researched and authoritative content that looks closely at both the user’s needs and what signals google is giving you to what needs to be included on the page.
Next, you’ll see internal linking. The structure of your overall site and the links to your main pages are key. Internal links are a very strong signal that tell google what the most important pages are on your site. They’re also helpful for users who are trying to find your most useful information.
This brings us to the next point, user experience. Like we mentioned above, Google has become a task completion engine. This means that Google wants to help users solve the problem they’re querying. If your information efficiently solves users’ issues, it will rank.
On-Page Factors
Here are typical variables we like to play with:
- Page titles
- Headings
- Outbound links to authority pages
- Anchor text on internal and external links
- Body copy
- Bold / Italic Text
- Structured Data
- Numbered / Bulleted Lists
- Image + Video embeds
- Alt-text on images
- Image filenames
We go into these in more detail in our free SEO Guide.
SEO Reading + Resources
Fuel Your Photos Facebook Group
Free SEO for Photographers Guide
Ahrefs Blog (popular SEO tool)
Citations
Who Coined The Term SEO? – Search Engine Land
Word Vectorizing and Statistical Meaning of TF-IDF – Becoming Human
Google Duplex: An AI System for Accomplishing Real-World Tasks Over the Phone
How Google Search Ranking Works
Bonus Step: Take our SEO course.
We’ve condensed years of training into a 17 lesson course. The lessons are task based and have defined goals. The course has text, video, and screenshot examples for all types of learners. The course community is a supportive place to ask questions and discuss techniques.
FAQ
Each page has a “bid” calculated. This bid is calculated by multiplying hundreds of factors together. Each factor can have multiple signals. Then spam results are removed and search features are decided on.
While these can be somewhat important for image search rankings, this is typically not necessary if the page contains useful content. Google can understand the image contents using machine learning and onpage signals.
You don’t need to blog more often to improve your SEO. You just need to make sure that your blog content is useful information, well researched, and fits the user’s intent.
While pagespeed can be used in a tie breaker during the ranking process, it is most important due to its affect on user metrics. Users greatly prefer fast websites and will bounce if your site takes too long to load.
